- Home
- News Releases
- Back Issues
- June FY2024
- Compilation of the Smart Manufacturing Development Guideline (SMD Guideline)
Compilation of the Smart Manufacturing Development Guideline (SMD Guideline)
June 28, 2024
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) and the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO) jointly formulated the Smart Manufacturing Development Guideline (SMD Guideline) targeting manufacturing companies and hereby release the guidelines as of June 28, 2024. The guidelines focus on helping companies to make plans and conceptual designs for the application and introduction of digital solutions, placing the identification of challenges in management and operational reform as a starting point, thereby assisting manufacturing companies in solving the challenges they face in management.
1. Background
In recent years, manufacturing companies have been affected by rapid changes in the social environment and increased uncertainty. As a result, they have been facing management and operational challenges, including supply chain disruptions, a decline in productivity caused by labor shortages, and an increase in management costs associated with these challenges.
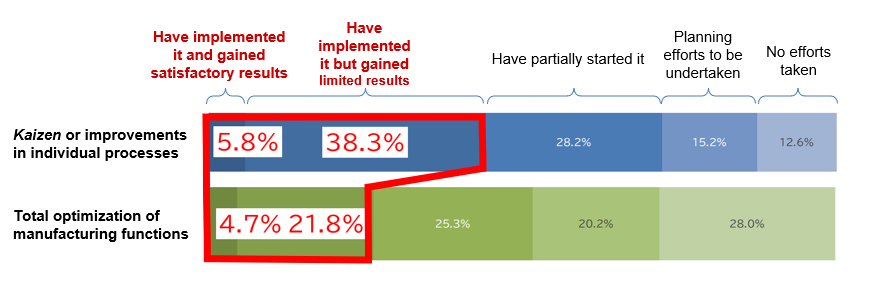
As a way to solve these challenges, manufacturing companies can make use of digital solutions, which have been advancing in recent years, to achieve business reform. However, they may find it difficult to fundamentally solve the challenges if they make efforts simply by focusing on Kaizen or improvements in individual processes based on existing departmental functions and operations, rather than by identifying challenges in management and operational reform.
In order to fundamentally solve challenges in management and operational reform, manufacturing companies need to conduct the total optimization of business by taking a panoramic view of not only the manufacturing department but also the entire manufacturing process. Nevertheless, many manufacturing companies seem to have been stuck with their hands folded as they face bottlenecks, lacking both personnel who can comprehensively consider the functions of each department and know-how on how to proceed with business reform that strikes a balance between digital solutions and manufacturing reform.
2. Outline of the guidelines
The guidelines contain the following key points.
- The importance of aiming for the total optimization of business by taking a panoramic view of the entire manufacturing process, including not only manufacturing functions but also peripheral functions, e.g., procurement, development, design, and sales (the main text of the guidelines).
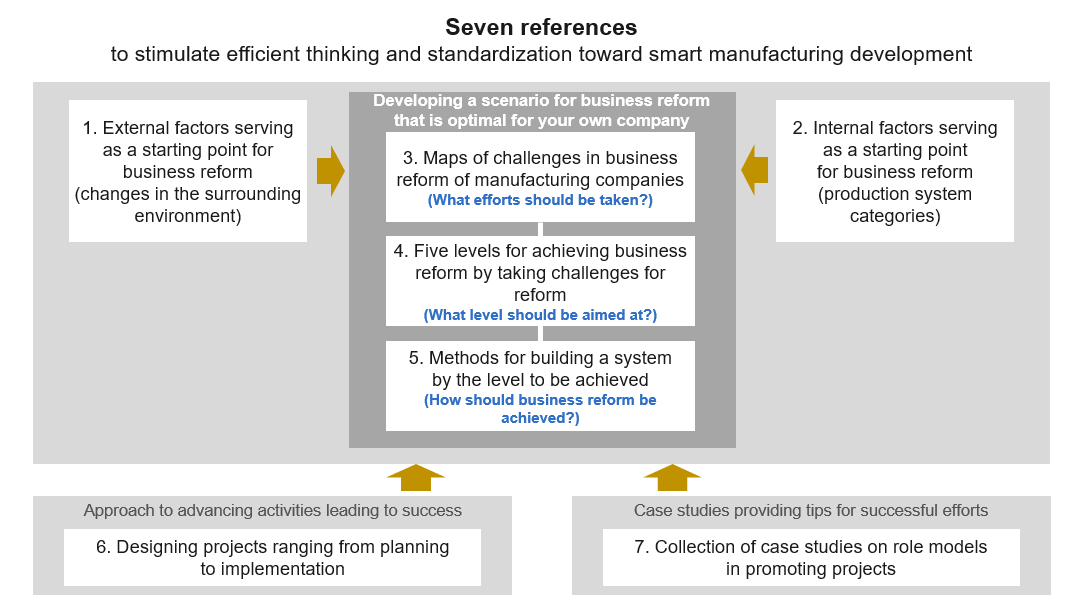
- Lists of challenges in management and those in operational reform by category based on the results of a questionnaire survey, which were prepared based on the stance that companies should take efforts based on challenges in management and those in operational reform (References 1 and 3).
- Challenges in management and those in operational reform that companies should address by production system category (References 1 and 2), an overview of efforts tailored to companies’ achievement levels (References 4 and 5), and processes for designing projects, points to note, and a collection of case examples (References 6 and 7), all of which will help readers to smoothly choose specific challenges and shift to design projects while keeping the stance of taking a panoramic view and carrying out efforts specifically.
The goal of business reform by making use of digital solutions may vary depending on the environment in which individual companies are placed, including the sizes of the companies and their business, their industry, the position in the supply chain, and their management polices. With this in mind, the guidelines, which do not aim to provide uniform answers, provide references to support manufacturing companies in proactively considering approaches to depicting and advancing a pathway for business reform that is appropriate for them.
Readers of the guidelines are expected to be top-level managers as project owners responsible for a smartization project, personnel in a managerial post playing a leading role, and leaders of practical operations in individual departments. METI expects that the guidelines will serve as a guide for these readers, thereby encouraging them to aim at business reform by applying and introducing digital solutions.
Even after the publication of the guidelines, METI and NEDO will continue to refine them by requesting manufacturing companies to apply them in order to examine the effectiveness of the guidelines and by collecting information from IT vendors. Some manufacturing companies, which have cooperated with METI in the preliminary examination of the effectiveness of the guidelines, provided feedback noting that the guidelines were useful as a tool for planning business reform targeting all functions involving manufacturing across the borders of the company while others showed their expectations for the development of a manual on how to use the guidelines and output formats.
3. Related Link
Division in Charge
Manufacturing Industries Strategy Office, Manufacturing Industries Bureau