- Home
- News Releases
- Back Issues
- October FY2025
- OT Security Guidelines for Semiconductor Device Factories Compiled in Japanese and English Versions
OT Security Guidelines for Semiconductor Device Factories Compiled in Japanese and English Versions
October 24, 2025
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) has compiled and released the OT Security Guidelines for Semiconductor Device Factories (the Guidelines) both in Japanese and English. These are factory security measure guidelines for Japan’s semiconductor industry, which are in line with various global security standards for the semiconductor industry. Moving forward, METI will explore linking the security measure standards outlined in the Guidelines to the requirements of its investment promotion-related policies for the semiconductor industry.
1. Background
Cyberattacks have become increasingly diverse and sophisticated, leading to attacks on various control systems with operational technology (OT), which result in damage such as halts to factory production. Additionally, there is an increasing risk that various confidential information for development (i.e., intellectual property) could be leaked through cyberattacks. Considering the economic and national security importance of the semiconductor industry, as well as the growing cyberthreats and risks we face today, it is imperative to promote security measures, including countermeasures against advanced cyberattacks.
On the international stage, the global semiconductor industry association SEMI has developed the E187/E188 Standards for semiconductor manufacturing equipment. Furthermore, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) is working on the development of a semiconductor manufacturing profile for its Cybersecurity Framework 2.0 (NIST CSF 2.0).
In Japan, METI formulated and published the Cyber/Physical Security Guidelines for Factory Systems in 2022, targeting generic assembly-type factories. However, the guidelines are not suitable for semiconductor factories, which are generally categorized as process automation (PA) type factories, characterized by large-scale operations and a high number of manufacturing devices that utilize general-purpose operating systems (OS).
In light of this awareness of the issues at hand, METI has convened the Semiconductor Industry Sub-Working Group under the Industrial Cybersecurity Study Group, chaired by Professor Ezaki from the University of Tokyo, since November 2024. These meetings have involved various domestic and international companies and organizations, including semiconductor device manufacturers and suppliers of semiconductor manufacturing equipment. The purpose of these discussions is to explore the optimal approaches to security measures for OT systems in Japan's semiconductor device factories. The outcome of the discussions was compiled into the draft OT Security Guidelines for Semiconductor Device Factories (both in Japanese and English) designed to serve as factory security measure guidelines for Japan’s semiconductor industry and to align with various global security standards for the semiconductor industry. The draft guidelines were then published for public comment from Friday, June 27, to Tuesday, August 26, 2025, modified as necessary based on the feedback from the public, and have now been compiled as the finalized guidelines.
2. Overview of the Guidelines
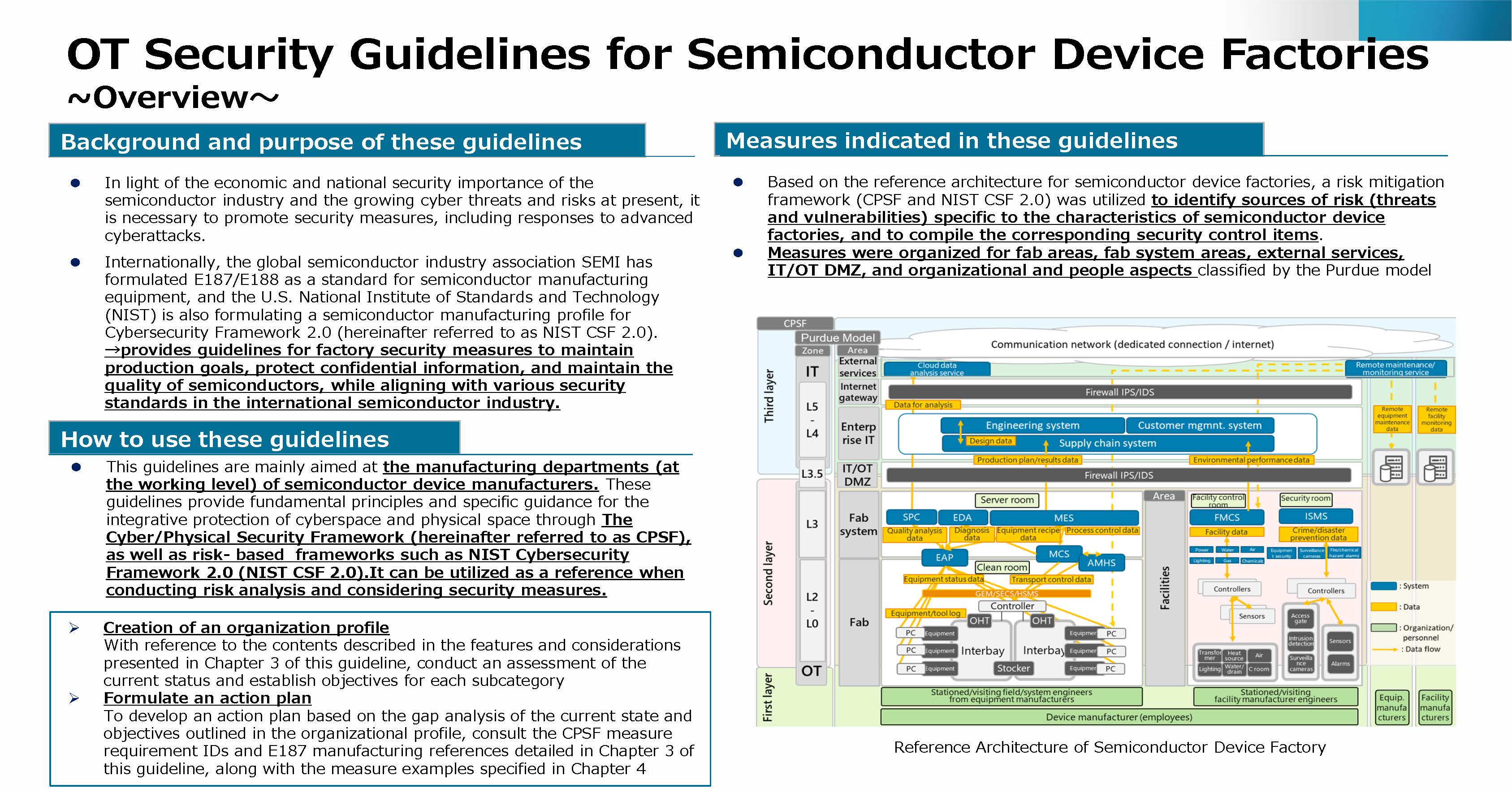
The Guidelines are primarily intended for the manufacturing divisions of semiconductor device manufacturers, particularly at the practitioner level. The Guidelines outlined the necessary factory security measures to achieve an action level addressing the most sophisticated threats, such as advanced persistent threat (APT) groups supported by nation-states. The Guidelines focus on safeguarding the key points of maintaining production goals (supply responsibilities), protecting confidential information, and maintaining the quality of semiconductors, and align with various security standards, including E187/E188 and NIST CSF 2.0.
The Guidelines are expected to be utilized in the general process of advancing security measures in factories. For instance, they will be used during risk analyses that employ risk-based cybersecurity frameworks, such as the Cyber/Physical Security Framework (CPSF) and NIST CSF 2.0, as well as for considering specific security measures.
The measures outlined in the Guidelines can be broadly divided into the following two points.
- Security measures addressing risk sources (threats and vulnerabilities) specific to semiconductor device factories, identified by leveraging risk management frameworks (CPSF and NIST CSF 2.0) based on the reference architecture for semiconductor device factories.
- Measures for the following areas classified under the Purdue model: fab areas, fab system areas, external services, IT/OT DMZ, and organization/human aspects.

Moving forward, METI will explore linking the security measure standards outlined in the Guidelines to the requirements of its investment promotion-related policies for the semiconductor industry.
Related Materials
- Summary of OT Security Guidelines for Semiconductor Device Factories: Japanese Version(PDF:3,368KB)

- OT Security Guidelines for Semiconductor Device Factories: Japanese Version(PDF:8,381KB)

- Summary of OT Security Guidelines for Semiconductor Device Factories: English Version(PDF:3,069KB)

- OT Security Guidelines for Semiconductor Device Factories: English Version(PDF:5,023KB)

Related Links
- Industrial Cybersecurity Study Group Working Group 1: Semiconductor Industry Sub-Working Group (in Japanese)
- Cyber/Physical Security Framework (CPSF) and its Deployment (in Japanese)
- OT Security Guidelines for Semiconductor Device Factories (in Japanese)
Divisions in Charge
Cybersecurity Division, Commerce and Information Policy Bureau
IT Industry Division, Commerce and Information Policy Bureau