- Home
- Policies
- Policy Index
- Transition Finance
Transition Finance

Japan Climate Transition Bond Framework
- The government of Japan has developed the "Japan Climate Transition Bond Framework" for the world's first government-labeled transition bond to be issued as a "Japan Climate Transition Bond".
- More than 150 trillion yen of public-private investment is required over the next 10 years for GX investment, and Japan have decided to issue 20 trillion yen of GX Economy Transition Bonds to finance these investments.
- The GX Economy Transition Bonds are not limited to the integrated issuance of existing JGBs as the same financial instruments, but also issue "climate transition bonds" that have been certified by an external review provider to assess (Second Party Opinion) for compliance with international standards as individual bonds.
➡︎ Japan Climate Transition Bond Framework![]()
➡︎ Second Party Opinion (DNV![]() ) (JCR
) (JCR![]() )
)
➡︎ Japan Climate Transition Bonds Allocation Report for FY2023 Issuance ![]()
➡︎ Japan Climate Transition Bonds(Ministry of Finance)![]()
➡︎ (reference) Pathways to Japan’s Green Transformation ![]()
1. Transition Finance Overview
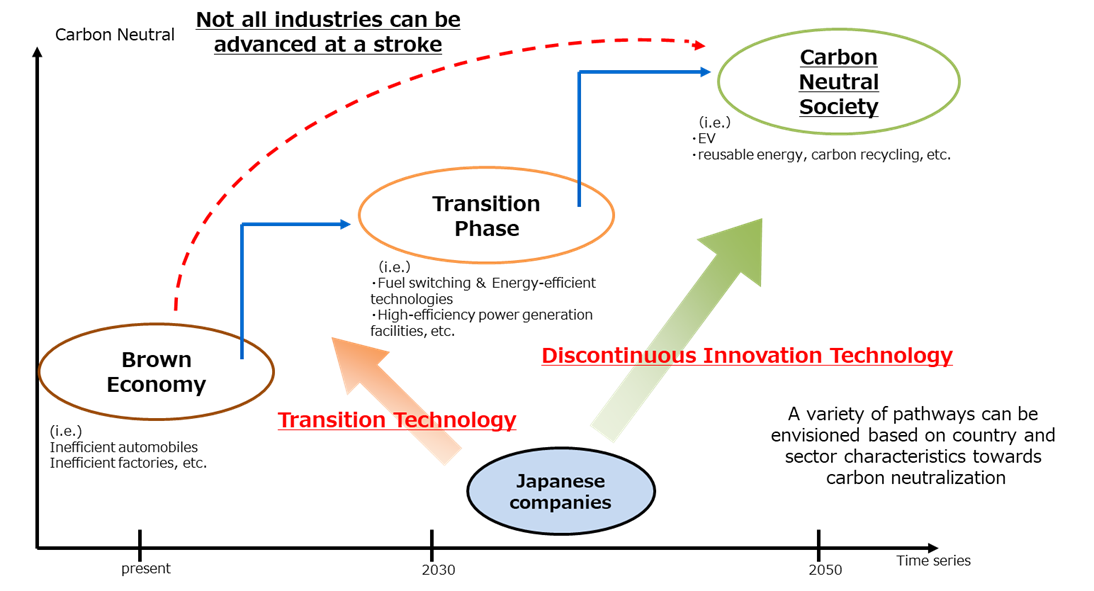
- A "decarbonized society" is a vision of the future that should be pursued on a global scale and requires a large amount of financing.
- In Japan, in order to realize a carbon-neutral and decarbonized society by 2050, it is important to finance the transition toward steady decarbonization, including energy conservation and fuel switching, mainly in GHG-intensive industries, in addition to efforts for projects that are already at a decarbonized level (green), such as renewable energy. Not all countries, regions, and industries can decarbonize at once in terms of both technology and cost, and it is necessary to maximize emission reductions by adopting transitional technologies.
- Transition finance is a new financing approach that aims to support companies that are trying to steadily reduce GHG emissions in accordance with a long-term strategy to achieve a decarbonized society.
2. Basic Guidelines on Climate Transition Finance
(1) Positioning of the Basic Guidelines

- The Basic Guidelines are geared toward operating companies, securities firms, banks, evaluation agencies, investors, etc., to enable such companies to label (name) their low and decarbonization investments as "transition bonds/loans" and raise funds for them.
- As transition finance is relatively new, promoting and ensuring its credibility will help it become established as a financing tool for decarbonization, especially in sectors where emission reductions are difficult. It will contribute to Japan's goal of achieving carbon neutrality by 2050 by introducing more financing.
- The Basic Guidelines were formulated in May 2021 in collaboration with the Financial Services Agency and the Ministry of the Environment, based on the international principles of the Climate Transition Finance Handbook released in December 2020 by the International Capital Markets Association (ICMA), which publishes the Green Bond Principles and other guidelines.
(2) Overview of the Basic Guidelines
- This section summarizes issues related to disclosure, disclosure items and supplements, and matters related to third-party review for the four elements (strategy and governance, materiality, scientific basis, and transparency), as with the ICMA.
- In the Basic Guidelines, transition finance does not focus solely on the use of proceeds and KPIs, but rather on the company's "transition strategy" toward decarbonization and the credibility and transparency of implementing that strategy in a comprehensive manner.
- In addition to internationally recognized scenarios from the IEA and other organizations, the guidelines allow reference to Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs) and sectoral roadmaps from other countries that are consistent with the Paris Agreement.

(3) Positioning of Transition Finance
- Although the Use of Proceeds may include a wide range of applications, it can be said that transition finance is for entities that are more ambitious in terms of their future as they are required to have a clear strategy for realizing long-term goals that are consistent with the Paris Agreement.
- Transition finance is therefore positioned, like green finance, as an extremely important tool for the realization of a decarbonized society.
- Basic Guidelines on Climate Transition Finance(Full)【FY2025】(PDF:5,025KB)

- Key Points of the Basic Guidelines Revision【FY2025】(PDF:1,307KB)

- Basic Guidelines on Climate Transition Finance (Full)【FY2021】(PDF:3,199KB)

- Basic Guidelines on Climate Transition Finance (Summary)【FY2021】(PDF:538KB)

- ICMA Climate Transition Finance Handbook

3. Roadmap for Promoting Transition Finance
- The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry (METI) developed a roadmap to provide a concrete direction for transition toward achieving carbon neutrality in 2050 for GHG-intensive industries.
- It is assumed that companies will refer to this roadmap when considering climate change measures using transition finance.
- The roadmap is expected to assist financial institutions in determining whether a company's strategies and initiatives toward decarbonization qualify for transition finance when the company raises funds.
(1) Economic and Industrial Sectors
| Iron and Steel | English |
Japanese |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical | English |
Japanese |
| Power | English |
Japanese |
| Gas | English |
Japanese |
| Oil | English |
Japanese |
| Pulp and Paper | English |
Japanese |
| Cement | English |
Japanese |
| Automobile | English |
Japanese |
(2) Other Sectors
In other industrial sectors, there are roadmaps and other documents that show technologies and directions toward decarbonization, which can be used for transition finance.
- Roadmap to Zero Emission from International Shipping (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism) (under review)

- Domestic Marine Transport/Summary of the Study Group for Promoting Carbon Neutral Domestic Marine Transport (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism) [in Japanese]

- Aviation Sector/Procedure Chart for the Promotion of Decarbonization of Aviation (Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism) [in Japanese]

4. Transition Finance Follow-up Guidance
(1) Positioning of the Follow-up Guidance

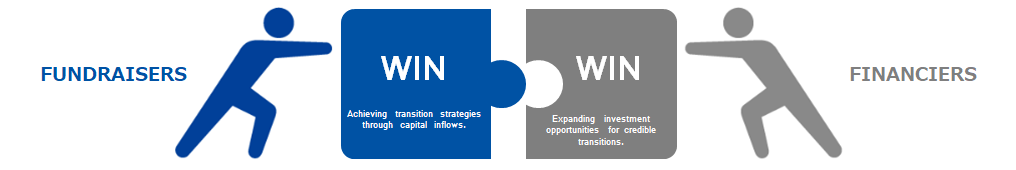
- To encourage financial institutions to promote efforts that contribute to decarbonization in the actual economy through transition finance, the key elements are for companies to build and disclose highly credible transition strategies and to encourage financial institutions to support and facilitate the steady accomplishment of the strategies through dialogues with those companies.
- The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, in June 2023, jointly with the Financial Services Agency and the Ministry of the Environment, aiming to improve the credibility and effectiveness of transition finance, has formulated a Guidance on Follow-ups Involving Transition Finance - Toward Better Dialogues with fundraisers as a guide to secure the steady accomplishment of transition strategies and the improvement of corporate value particularly after the provision of funds.

(2) Overview of the Follow-up Guidance
- Transitions by hard-to-abate sectors (those facing difficulties in accomplishing decarbonization in one bound) aim for ambitious carbon neutrality goals based on the best judgment at the time and continues their efforts and investment on transition technologies which therefore requires dynamic approach.
- The follow-up on transition finance involves a trust-building dialogue between financiers and fundraisers for decarbonization funding and should not be seen as an adversarial process. Therefore, this document provides the perspectives and matters that financiers should consider during follow-up activities.
- The target audience includes a wide range of financiers, with a particular emphasis on bond investors. This document covers how to prepare for a dialogue and provides comprehensive and practical information on the timing and method of dialogue.
- In the Follow-up activities, it is important to keep in mind the differences in sector characteristics. The Guidance addressed not only the individual sectors important concepts to understand the relationships and dynamics of the sectors. Summarized the Sectoral Technology Roadmaps in the appendices.
- Transition Finance Follow-up Guidance(PDF:2,060KB)

- Transition Finance Follow-up Guidance (Overview)(PDF:442KB)

5. Addressing the Challenges of Financed Emissions
(1) Background
- International financial alliances such as Glasgow Financial Alliance for Net Zero (GFANZ), endorsed by major financial institutions, require ambitious targets for financial institutions to reduce their emissions to net zero, including indirect the emissions come from their borrowers/investees (financed emissions). Some financial institutions may refrain from financing hard-to-abate sectors based on their concern of a temporary increase in financed emissions, which could result in hindering the transition of such sectors.
- With this problem awareness, the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, the Financial Services Agency, and the Ministry of the Environment, in February 2023, jointly established the “Japan Public and Private Working Group on Financed Emissions to Promote Transition Finance”, consisting of 10 members from globally-operating financial institutions and other entities, under the Taskforce on Development of the Environment for Effective Transition Finance.
- The working group examined and discussed possible solutions to the challenges above, including effective approaches to the specific calculation and disclosure of financed emissions, and the utilization of indicators other than financed emissions, and in October 2023, compiled discussion results into a paper titled “Addressing the Challenges of Financed Emissions.”

(2) Overview
- This paper organizes the role of financial institutions in achieving carbon neutrality and the characteristics of financed emissions, and, based on these, it presents possible solutions to the challenges of financed emissions by categorizing such solutions into the two groups of (1) approaches on calculation and disclosure of financed emissions and (2) use of multiple metrics, which are expected to help readers to appropriately evaluate and promote financing towards innovation and transition efforts by hard-to-abate sector.
- Addressing the Challenges of Financed Emissions(PDF:1,292KB)

- (Related Material) Creating an Enabling Environment to Scale-up Transition Financing to Accelerate Decarbonization of Hard-to-Abate Sectors(PDF:322KB)

6. Transition Finance Model Project・Subsidy
(1) Overview
In order to promote transition finance, this project subsidizes the assessment costs for cases that conform to the Basic Guidelines and are deemed to have model qualities and publicizes information of such cases as a good model.
(2) Model Cases
The following projects were selected as model cases as a result of rigorous screening by a third-party committee (Modelability Model Quality Examination Committee).
(FY2021)
| Companies | Overview | Second Party Opinion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.Nippon Yusen Kabushiki Kaisha | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 2.Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 3.Kawasaki Kisen Kaisha, Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 4.JFE Holdings, Inc. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 5.Japan Airlines Co., Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 6.Sumitomo Chemical Company, Limited | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 7.Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 8.JERA Co., Inc. | English |
Japanese |
English① English② |
Japanese① Japanese② |
| 9.IHI Corporation | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 10.Osaka Gas Co., Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 11.Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 12.Idemitsu Kosan Co., Ltd | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
(3) Subsidy for global warming countermeasures promotion project
The following companies were selected as recipients of subsidy for global warming countermeasures promotion project.(FY2022)
| Companies | Overview | Second Party Opinion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.Hokuriku Electric Power Company | English |
Japanese |
ー | Japanese |
| 2.TOHO GAS Co., Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 3.Tokyo Gas Co., Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 4.Kirin Holdings Company, Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 5.Japan Airlines Co., Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 6.TAIHEIYO CEMENT CORPORATION | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 7.Kawasaki Kisen Kaisha, Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 8.Mitsubishi HC Capital Inc. | English |
Japanese |
ー
|
Japanese LOC(Japanese) |
| 9.Hokkaido Electric Power Co., Inc. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
➡︎ Transition Finance 2022 market overview![]()
(FY2023)
| Companies | Overview | Second Party Opinion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.Kawasaki Heavy Industries, Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
ー | Japanese |
| 2.Mitsubishi Materials Corporation | English |
Japanese |
ー | Japanese |
| 3.Chubu Electric Power Co., Inc. | English |
Japanese |
ー | Japanese |
| 4.Mitsui O.S.K. Lines, Ltd. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 5.JFE Holdings, Inc. | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 6.Mazda Motor Corporation | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
| 7.Kansai Electric Power Company | English |
Japanese |
English |
Japanese |
➡︎ Transition Finance 2023 market overview![]()
(FY2024)
| Companies | Overview | Second Party Opinion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.Sanyo Special Steel Co., Ltd. | Withdrawn due to issuer's circumstances (SA: Mizuho Securities) |
Not disclosed (Rating and Investment Information, Inc.) |
||
| 2.Teijin Limited.pdf | English |
Japanese |
ー | Japanese |
(FY2025)
| Companies | Overview | Second Party Opinion | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.NS UNITED KAIUN KAISHA, LTD. | TBD | Japanese |
ー | Japanese |
| 2.Daio Paper Corporation | TBD | Japanese |
ー | Japanese |
| 3.TBD | TBD | |||
| 4.JFE Holdings, Inc. | TBD | Japanese |
ー | Japanese |
Last updated:2026-01-29